Advanced Splitter and Multicast with Aggregation Strategies for REST Composition Apache Camel EIP
Here is an example of Camel mediation with more advanced use of Splitter and Multicast EIP’s as well Aggregation strategies to compose REST services. The composed service is simultaneously exposed using REST, SOAP, and JMS endpoints. The camel-xmljson data format is used to provide flexible marshalling for both JSON and XML representations for the REST endpoint as well.
The exported route is available for download and there is a youtube design walk-through of the route available as well.
The use case is as follows:
- Whois Domain - ARIN RESTful Web Service API
- Query IP address
- Capture Organization & NetRange
- Query Organization
- Capture Address City/State
- Ping first 10 IP addresses in NetRange
- Return results of ping
Virtual Endpoints
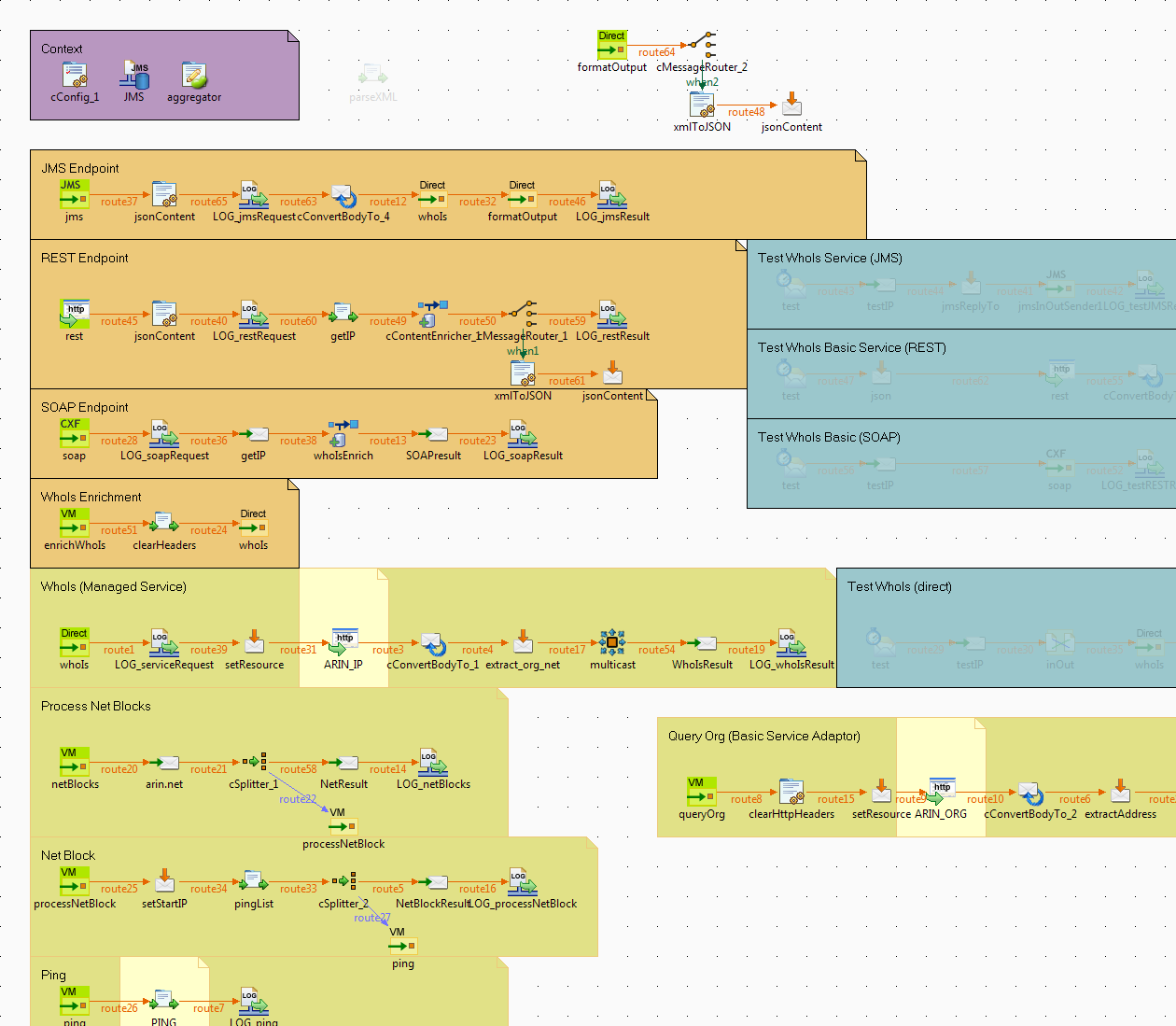
The actual service is mediation route is implemented as a service which is exposed using multiple transports including JMS, SOAP, and REST. The external endpoints make use of a common logical endpoint exposed via Direct: transport. Each endpoint exposes the same Managed Service in a manner appropriate for the semantics of that transport. Endpoint routes are at the top and shown in orange.
Test Routes
The routes shown in Blue are test routes.
There are test routes for both the exposed Basic Service endpoints as well as the underlying logical service implementation.
Mediation Routes
The actual mediation routes and implementation shown in tan. Calls to the external services are highlighted in yellow boxes.
Splitter Aggregator
Many Camel components support aggregation strategies.
It is not always obvious to new users that there are two distinct sub-routes for these elements.
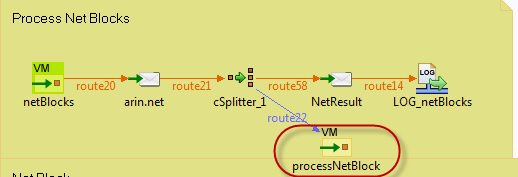
For example, in the route segment below the splitter will split the original composite message and route individual messages to the processNetBlocks endpoint.
There could be potentially very many messages being processed independently via the path shown in blue since the splitter has a 1:m relationship between inbound and outbound messages.
When these individual messages are finished processing they can optionally be aggregated by specifying the Aggregation Strategy in the Splitter component.
The resulting aggregated result is then routed as a single messsage to the next step on the original route shown by the line in red.
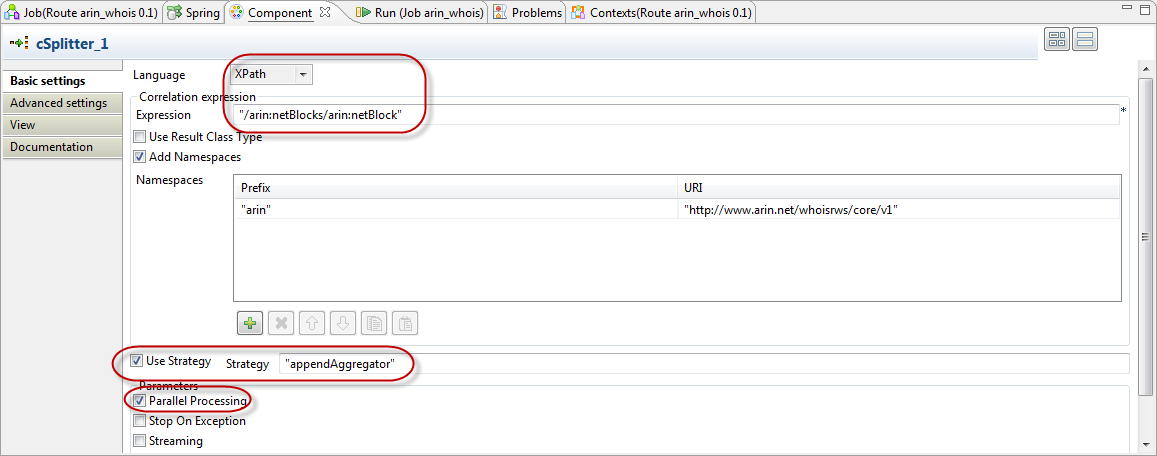
The splitter component configuration is shown below.
- The original xml message is parsed via the Xpath expression language. Namespaces are intiailized since they are used by the service.
- The “Use Strategy” checkbox has been selected and a custom appendAggregator specified. In this case the aggregation strategy is implemented as a class in the Code section of the Mediation perspective. But it could be any java bean or static method.
- Parallel Processing has been selected, so the multiple parsed messages may be processed independently.
- Each time a split thread finishes processing a sub-message, the result is returned to the Aggregation strategy which in this case simply appends it to the result.
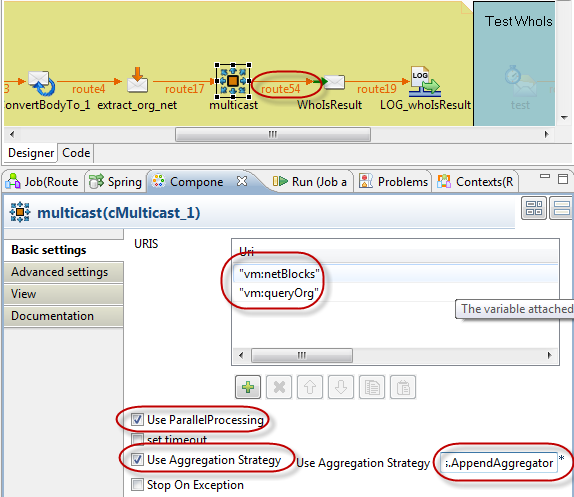
Multicast Aggregator
The Multicast component is for static routing to multiple endpoints. In this case, the original composite service request is mediated by the bus and passed to two service invocations. The first results in additional ping requests based on the NetBlock data elements. The second is an invocation of the ARIN service to retrieve additional organization info. These operations can proceed in parallel based on the design, so they are invoked with the multicast operation since they are known in advance. If the operations were dynamic and needed to be determined at runtime then the Recipient List would be a better choice.
The multicast component has a similar approach to aggregation. If an aggregator is specified, the results of the aggregation strategy will be applied when each multicast target returns. The multicast targets can be specified in URI list in the Component tab of UI.